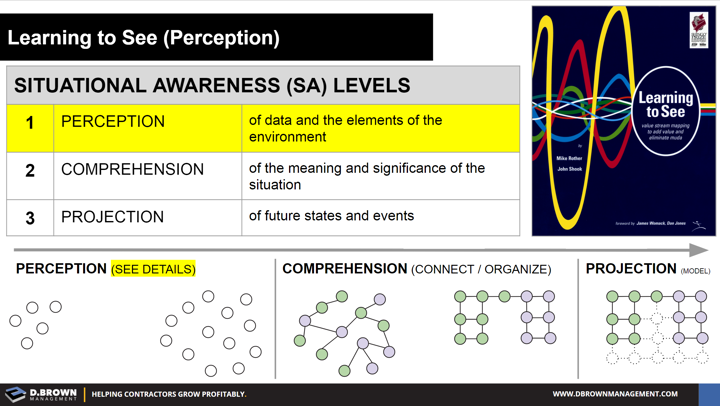
It is critical for project teams to develop a complete 5D model of the project in their minds.
This is called Situational Awareness and includes three basic layers:
- PERCEPTION of data and the elements of the environment.
- COMPREHENSION of the meaning and significance of the situation.
- PROJECTION of future states and events.
If you are training yourself or someone else start at 1st layer and focus on seeing more elements of the environment. Ask questions that stretch yourself and others to see things. Use checklists to help train. Create drills to improve both the quantity and quality of elements seen as well as speed.
The lean body of knowledge starts with “seeing waste” in the value stream. A great book on this topic is called “Learning to See” and Paul Akers has a great talk on this called “Lean is Simple”